Unlock IoT Device Management: A Comprehensive Guide + Tips
Ever wondered how the vast network of interconnected devices, from smart thermostats in our homes to sophisticated sensors in industrial plants, operate seamlessly? The answer lies in IoT device management, a critical discipline that ensures these devices function efficiently, securely, and reliably throughout their entire lifecycle.
This article delves into the core of IoT device management, exploring its key features, leading remote platforms, tangible benefits, and real-world examples. Understanding this multifaceted field is essential for anyone involved in deploying or managing IoT solutions, as it directly impacts the performance, security, and scalability of these increasingly vital systems.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive process of overseeing and remotely controlling IoT devices throughout their lifecycle. |
| Key Objectives | Ensuring efficient, secure, and reliable operation of IoT devices. |
| Core Processes | Equipping, validation, configuration, monitoring, and analysis of connected devices. |
| Essential Features | Remote software updates, security patching, rebooting, factory resets, device authentication, and authorization. |
| Benefits | Streamlined device management, enhanced security, improved network performance, and reduced downtime. |
| Challenges | Device heterogeneity, interoperability issues, network performance, security vulnerabilities, and integration with existing IT systems. |
| Solutions | Centralized management platforms, remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools, secure authentication protocols, and structured approaches to risk mitigation. |
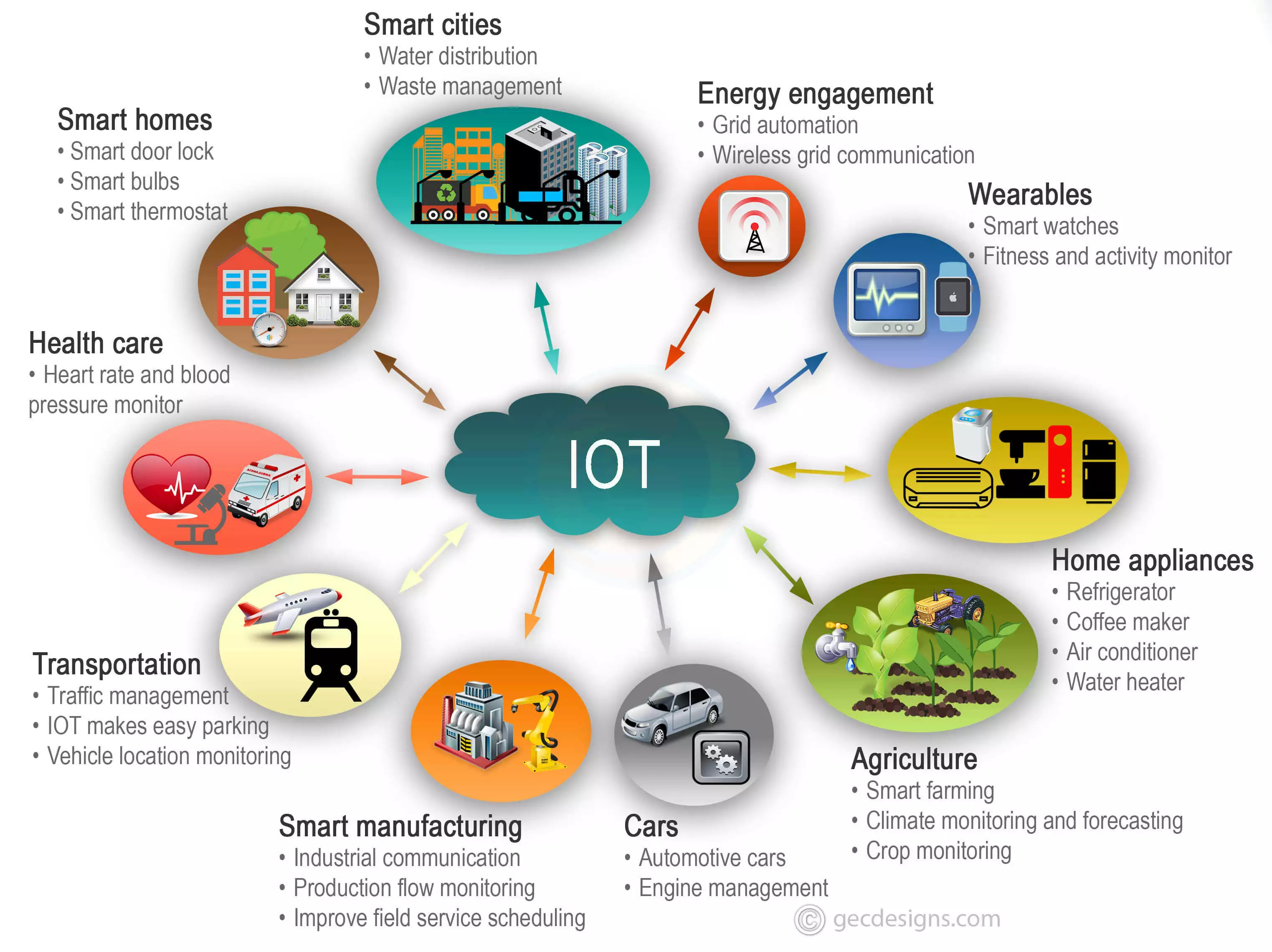
| Examples | Smart sensors, cameras, wearables, industrial equipment, and manufacturing machinery. |
| Impact | Influences how individuals interact with and manage their environments, both at home and at work. |
IoT device management encompasses a range of processes, tools, and technologies designed to provision, monitor, and maintain the ever-expanding universe of connected objects, often referred to as IoT endpoints or edge devices. These devices, ranging from simple sensors to complex industrial equipment, generate vast amounts of data and perform critical functions, making their effective management paramount.
- Ullu Web Series Your Ultimate Guide To Download Streaming Now
- Subhashree Sahu Mms Scandal Unveiling The Controversy 2024 Update
A fundamental aspect of IoT device management is the ability to remotely update software on devices deployed in the field. This ensures that each device has access to the latest security patches and updates, maintaining the overall security posture of the network. Without this capability, organizations would face the daunting task of physically accessing and updating each device, a logistical nightmare for large-scale deployments.
The core of IoT device management involves a structured series of processes: equipping, validating, configuring, monitoring, and analyzing the connected devices within an IoT environment. The ultimate goal is to provide and support the full spectrum of their functional abilities, ensuring they operate as intended and deliver the expected value.
An effective and secure IoT device management solution is therefore highly valuable. Its basic requirements can be categorized into five key areas. First, devices need to be properly connected to the internet to become part of the IoT ecosystem. Second, the onboarding stage requires robust authentication and provisioning mechanisms to ensure only authorized devices are admitted to the network. Third, the solution should provide a centralized platform for remote management. Fourth, reliable and efficient network performance is crucial. Finally, the solution must address the inherent security challenges of IoT deployments.
- Hdmovieshub Is It Safe Risks Amp Legal Alternatives Guide
- Jackermans Mothers Warmth Ch 3 Release Date Heartfelt Story
The role of the IoT platform in remote management is pivotal. It acts as the central hub for interacting with and controlling devices, providing a unified interface for tasks such as restarting a device over the network, pushing software updates, and monitoring device performance. The platform streamlines operations and enhances visibility across the entire IoT infrastructure.
Challenges abound in managing IoT devices, especially when ensuring reliable and efficient network performance. IoT devices rely heavily on network connectivity to transmit data and receive instructions. However, the sheer diversity of devices and their compatibility with various network protocols can create interoperability challenges, hindering seamless communication and data exchange.
Remote device management platforms offer a suite of features designed to help IT teams maintain device security and performance. While IT staff can monitor device activity to provide support and troubleshoot issues, they may not always have direct control. However, IoT device management facilitates remote software updates, security patch deployments, reboots, and factory resets across an entire IoT fleet, empowering IT teams to proactively address potential problems.
Several platforms offer comprehensive IoT device management capabilities. AWS IoT Device Management, for instance, provides a secure and unified platform that streamlines the entire device management process. Similarly, other platforms offer features such as secure remote access from a centralized dashboard, automation capabilities, security management tools, mass firmware updates, and round-the-clock notifications for security breaches or other specified conditions.
Despite the benefits, remote device management (RDM) faces hurdles. Integrating different RDM tools with existing IT systems can be complex and time-consuming. Moreover, the heterogeneity of IoT devices, encompassing traditional computing devices used in offices and remote settings, internet of things devices such as smart sensors and cameras, and network infrastructure components like routers and switches, adds to the management complexity.
According to Lewis, the Internet of Things (IoT) represents the integration of people, processes, and technology with connectable devices and sensors to enable remote monitoring, status updates, manipulation, and evaluation of trends. The term "Internet of Things" was independently coined by Kevin Ashton of Procter & Gamble, highlighting the significance of this technological revolution.
Strategies for acquiring IoT device remote management capabilities are crucial for success. It's essential to "ace" the entire process by adopting centralized management platforms. These platforms act as the central point from which the entire control system operates, simplifying management and enhancing visibility.
With the proliferation of sensors and devices, IoT monitoring systems require remote control features to manage devices from any location. Remote monitoring and management (RMM) is the technology used to observe and maintain IT infrastructure and IoT smart devices remotely. Monitoring is critical for ensuring efficient resource utilization and preventing outages.
Effective and secure IoT remote control demands a structured approach to mitigate risks and optimize performance. Security is paramount, with secure device authentication and authorization being essential to protect against unauthorized access. These devices, often referred to as smart devices, form the foundation of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the system of interconnected devices in the industrial sector.
Manufacturing machinery and devices used for energy management are integral components of the Industrial Internet of Things. Remote device management offers a comprehensive solution for managing these complex systems. For example, an IoT ecosystem can be utilized in a transport company to track vehicles, monitor fuel levels, and optimize routes, showcasing the transformative potential of IoT.
An IoT device management platform is critical for any IoT deployment involving more than a few devices. The platform should provide secure remote access from a dashboard, enable automation, streamline security management, facilitate mass firmware updates, and provide 24/7 notifications for security breaches and other critical conditions. It's a specialized solution tailored to the growing ecosystem of IoT devices, including smart sensors, wearables, and industrial equipment.
IoT remote monitoring significantly impacts how we interact with and manage our environments, whether at home or at work. From remotely adjusting the thermostat to monitoring critical industrial processes, IoT technology is reshaping the way we live and work. By carefully considering the features, benefits, and challenges of IoT device management, organizations can unlock the full potential of this transformative technology.
The adoption of centralized management platforms stands out as a key strategy for effective IoT device management. These platforms offer a unified interface for monitoring, controlling, and updating devices, simplifying complex tasks and enhancing overall efficiency. By centralizing management functions, organizations can reduce the operational burden and improve the scalability of their IoT deployments.
One of the primary advantages of IoT device management is the ability to perform mass firmware updates. This feature allows organizations to push updates to a large number of devices simultaneously, ensuring that all devices are running the latest software and security patches. Mass firmware updates are crucial for maintaining the security and reliability of IoT networks, as they can quickly address vulnerabilities and improve device performance.
Security is a paramount concern in IoT device management, and robust security measures are essential to protect against unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Secure device authentication and authorization protocols are critical for ensuring that only authorized devices are allowed to connect to the network. Encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems are also important components of a comprehensive security strategy.
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools play a vital role in IoT device management by providing real-time visibility into the health and performance of devices. RMM tools can track key metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, network connectivity, and battery life, allowing IT teams to proactively identify and resolve potential issues before they escalate into major problems. These tools often include alerting capabilities that notify IT staff when devices deviate from normal operating parameters.
Another key aspect of IoT device management is the ability to remotely troubleshoot and diagnose issues. This capability allows IT teams to remotely access devices, view logs, and run diagnostics to identify the root cause of problems. Remote troubleshooting can significantly reduce downtime and minimize the need for on-site visits, saving time and resources.
IoT device management also enables organizations to remotely configure and provision devices. This includes setting up network parameters, configuring security settings, and installing applications. Remote configuration simplifies the deployment process and ensures that devices are properly configured before they are put into service.
Effective IoT device management requires a holistic approach that considers all aspects of the device lifecycle, from initial deployment to ongoing maintenance and eventual decommissioning. This includes not only the technical aspects of device management but also the organizational and process-related considerations.
One of the key challenges in IoT device management is the sheer scale of IoT deployments. Many organizations are deploying thousands or even millions of devices, making it difficult to manually manage and monitor each device individually. This is where automation becomes essential. By automating routine tasks such as device provisioning, configuration, and monitoring, organizations can significantly reduce the operational burden and improve the efficiency of their IoT deployments.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) presents unique challenges and opportunities for device management. IIoT devices are often used in harsh environments and perform critical functions, requiring a high degree of reliability and security. IoT device management solutions for IIoT must be tailored to the specific requirements of industrial applications.
The integration of IoT device management with other IT systems is also important. This includes integrating with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and other business applications. Integration allows organizations to leverage the data generated by IoT devices to improve business processes and make better decisions.
In addition to the technical aspects of IoT device management, it's also important to consider the human element. IT staff need to be trained on how to use the device management tools and processes, and they need to have the skills and knowledge to troubleshoot and resolve device-related issues. Organizations should also establish clear roles and responsibilities for device management.
The future of IoT device management is likely to be shaped by several trends, including the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI and ML can be used to automate device management tasks, predict device failures, and improve security. For example, AI can be used to detect anomalies in device behavior and automatically take corrective action.
Another trend is the growing importance of edge computing. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, reducing the need to transmit data to the cloud. Edge computing can improve performance, reduce latency, and enhance security. IoT device management solutions must be able to support edge computing deployments.
The increasing adoption of 5G technology is also expected to have a significant impact on IoT device management. 5G provides faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, enabling new IoT applications and use cases. IoT device management solutions must be able to take advantage of the capabilities of 5G.
Finally, the emergence of new security threats is driving the need for more sophisticated security measures in IoT device management. Organizations must stay vigilant and continuously update their security protocols to protect against the latest threats. This includes implementing strong authentication mechanisms, encrypting data, and monitoring for suspicious activity.
In conclusion, IoT device management is a critical discipline for ensuring the efficient, secure, and reliable operation of IoT devices. By adopting a comprehensive approach to device management, organizations can unlock the full potential of IoT and transform their businesses.
- Tamilblasters Guide Stream Tamil Movies More Updated
- Anjali Arora Mms Video The Truth The Impact And Whats Next

Remote IoT Device Management Key Features & Benefits
Best Remote IoT Device Management Platform Examples Your Ultimate Guide
Secure Remote Access Best SSH Solutions For IoT Devices