Mydriasis: Causes, Symptoms & When To Seek Help Now
Ever looked in the mirror and noticed your pupils are larger than usual, seemingly without reason? Unexplained dilation of the pupils, known as mydriasis, can be a subtle sign of underlying health issues and should not be ignored.
Mydriasis, in its simplest terms, is the excessive or prolonged dilation of the pupil. The pupil, that black circle in the center of your eye, is responsible for controlling the amount of light that enters, shrinking in bright light and expanding in dim conditions. When mydriasis occurs, the pupil remains dilated, even in bright light, indicating a disruption in the normal pupillary response. It's crucial to differentiate this from the normal pupillary dilation that occurs when transitioning from a brightly lit environment to a darker one. This natural adjustment ensures optimal vision in varying light levels, but mydriasis represents a deviation from this expected behavior.
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Name | Dr. Anya Sharma (Example) |
| Specialization | Neuro-Ophthalmology |
| Education | MD, PhD in Neuroscience |
| Experience | 15+ years in diagnosing and treating neurological conditions affecting vision |
| Professional Affiliations | American Academy of Ophthalmology, North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society |
| Research Interests | Pupillary disorders, visual pathways, neurodegenerative diseases |
| Contact | (Example) anya.sharma@email.com |
| Website | American Academy of Ophthalmology |
The causes of mydriasis are varied and span a range of possibilities, from relatively benign to potentially serious. One common culprit is the use of certain medications. Many prescription and over-the-counter drugs can have mydriatic effects as a side effect. These include antihistamines, decongestants, antidepressants, and medications used to treat Parkinson's disease. Recreational drugs, such as cocaine, ecstasy, and LSD, are also known to induce mydriasis. It's essential to be aware of the potential side effects of any medication you are taking and to inform your doctor of any unusual changes in your vision, including persistent pupil dilation.
- Sneak Peek Mother Warmth Chapter 3 Jackermans Story Continues
- Unveiling Odia Mms Viral Trends Impact Amp Social Concerns Now
Beyond medications and recreational drugs, injuries to the eye or brain can also lead to mydriasis. Direct trauma to the eye can damage the iris muscles responsible for pupil constriction, resulting in a fixed, dilated pupil. Head injuries, strokes, or tumors can increase pressure within the skull, affecting the nerves that control pupillary function. In these cases, mydriasis may be accompanied by other neurological symptoms, such as headache, dizziness, confusion, or loss of consciousness. It's crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience dilated pupils following a head injury, especially if you also have other concerning symptoms.
In some instances, mydriasis can be a sign of a more serious underlying medical condition. For example, it can be associated with third nerve palsy, a condition that affects the nerve responsible for controlling several eye muscles, including the one that constricts the pupil. Third nerve palsy can be caused by a variety of factors, including aneurysms, tumors, and inflammation. Mydriasis can also occur as a result of Adie's tonic pupil, a benign condition in which one pupil is larger than the other and reacts slowly to light. While Adie's tonic pupil is usually harmless, it's essential to rule out other potential causes of mydriasis through a thorough medical evaluation.
Diagnosing the cause of mydriasis typically involves a comprehensive eye exam and a review of your medical history. Your doctor will assess your pupillary response to light, measure the size of your pupils, and check for any other abnormalities in your eye movements or vision. They may also ask you about any medications you are taking, any recent injuries you have sustained, and any other medical conditions you have. In some cases, additional tests, such as neuroimaging (MRI or CT scan), may be necessary to rule out underlying neurological causes.
- Bollyflix Your Guide To Bollywood Movies Dubbed Series Watch Now
- The Viral Buscar Kid Mom Cctv Video Whats The Buzz
The treatment for mydriasis depends on the underlying cause. If it is caused by a medication, your doctor may be able to adjust your dosage or switch you to a different medication. If it is caused by an injury, treatment may involve surgery to repair the damaged iris muscles. In some cases, no treatment is necessary, especially if the mydriasis is mild and not causing any significant symptoms. However, it's essential to follow up with your doctor regularly to monitor your condition and ensure that it is not worsening.
It's important to remember that mydriasis is a symptom, not a disease. While it can be a sign of a serious underlying medical condition, it can also be caused by relatively benign factors. If you notice that your pupils are persistently dilated, it's always best to consult with a doctor to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Self-treating mydriasis is not recommended, as it can delay the diagnosis and treatment of potentially serious underlying conditions.
One of the critical areas of concern regarding mydriasis is its potential association with neurological emergencies. In cases of severe head trauma or stroke, a fixed and dilated pupil can be a sign of brain herniation, a life-threatening condition in which brain tissue is squeezed past rigid structures within the skull. This is particularly concerning in unconscious patients, as it indicates significant pressure on the brainstem, which controls vital functions such as breathing and heart rate. In these situations, rapid diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent permanent brain damage or death. However, it's important to note that a fixed and dilated pupil in an awake patient is less likely to be due to herniation and may indicate other causes, such as direct trauma to the eye or pharmacologic dilation.
Pharmacologic dilation of the pupil is a common occurrence in ophthalmology and optometry practices. Eye doctors often use dilating eye drops to widen the pupils, allowing for a better view of the retina and other internal structures of the eye. These drops typically contain medications such as tropicamide or phenylephrine, which temporarily paralyze the iris muscles responsible for pupil constriction. The effects of these drops usually wear off within a few hours, but in some cases, the dilation can persist for longer, especially with stronger medications. Pharmacologic mydriasis is characterized by poor or no pupillary constriction to light or near stimuli. It's essential for eye doctors to carefully monitor patients after dilation and to provide instructions on how to protect their eyes from bright light until the effects of the drops have worn off.
Another important aspect of understanding mydriasis is differentiating it from other pupillary abnormalities, such as anisocoria. Anisocoria refers to unequal pupil sizes, where one pupil is larger than the other. While anisocoria can sometimes be a normal variation, it can also be a sign of underlying medical conditions, such as Horner's syndrome or third nerve palsy. It's important to note that mydriasis specifically refers to the dilation of one or both pupils, while anisocoria describes the difference in size between the two pupils. Both mydriasis and anisocoria can be caused by a variety of factors, and a thorough medical evaluation is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
The impact of mydriasis extends beyond the physical changes in the eye. It can also affect a person's vision and overall quality of life. Dilated pupils allow more light to enter the eye, which can lead to increased sensitivity to light, known as photophobia. This can make it difficult to function in bright environments and may necessitate the use of sunglasses or other protective eyewear. Mydriasis can also affect a person's ability to focus, especially on near objects. This is because the pupil plays a role in accommodation, the process by which the eye adjusts its focus for different distances. Dilated pupils can impair accommodation, leading to blurry vision and eye strain. In addition to these visual symptoms, mydriasis can also be a source of anxiety and concern, especially if the underlying cause is unknown.
The advent of advanced ophthalmic technology has greatly improved the diagnosis and management of pupillary disorders, including mydriasis. Devices such as pupillometers can accurately measure pupil size and reactivity, providing valuable information about pupillary function. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) can be used to image the iris and other structures of the eye, helping to identify any abnormalities that may be contributing to mydriasis. Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, can be used to visualize the brain and identify any underlying neurological causes. These advanced technologies allow doctors to make more accurate diagnoses and develop more effective treatment plans for patients with mydriasis.
In addition to traditional medical treatments, there are also some lifestyle modifications that can help manage the symptoms of mydriasis. Wearing sunglasses or other protective eyewear can help reduce light sensitivity and improve comfort in bright environments. Avoiding exposure to known triggers, such as certain medications or recreational drugs, can help prevent mydriasis from occurring. Getting regular eye exams can help detect any underlying eye conditions that may be contributing to mydriasis. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress, can also help improve overall eye health and reduce the risk of developing pupillary disorders.
Research into the causes and treatments of mydriasis is ongoing. Scientists are continuing to investigate the complex mechanisms that control pupillary function and to develop new and innovative ways to treat pupillary disorders. For example, researchers are exploring the use of gene therapy to treat certain genetic conditions that can cause mydriasis. They are also developing new medications that can selectively target the iris muscles responsible for pupil constriction, without causing other side effects. As our understanding of mydriasis continues to grow, we can expect to see even more effective treatments become available in the future.
Beyond the direct medical implications, understanding mydriasis also touches upon broader aspects of human physiology and psychology. The pupil's response to light and other stimuli is intricately linked to the autonomic nervous system, which controls many of the body's involuntary functions, such as heart rate, breathing, and digestion. Changes in pupil size can reflect changes in the activity of the autonomic nervous system, providing clues about a person's emotional state, level of arousal, and cognitive workload. For example, studies have shown that pupils dilate when people are engaged in challenging mental tasks or experiencing strong emotions, such as fear or excitement. These findings have implications for a variety of fields, including human-computer interaction, marketing, and lie detection.
The use of mydriatic agents also plays a crucial role in the management of various eye conditions. In addition to their use in routine eye exams, dilating eye drops are often used to treat inflammatory conditions of the eye, such as uveitis. By paralyzing the iris muscles, these drops can help reduce pain and spasm, allowing the eye to heal more effectively. Mydriatic agents are also used to prevent adhesions from forming between the iris and the lens, a complication that can occur after eye surgery or injury. The choice of mydriatic agent depends on the specific condition being treated and the individual patient's needs.
The differential diagnosis of mydriasis can be challenging, as it encompasses a wide range of potential causes. It's essential for doctors to carefully consider all of the possible explanations for a patient's dilated pupils and to perform a thorough evaluation to arrive at an accurate diagnosis. In addition to the causes already mentioned, other conditions that can cause mydriasis include botulism, angle-closure glaucoma, and certain types of brain tumors. The presence of other symptoms, such as headache, vision changes, or neurological deficits, can help narrow down the list of possible diagnoses. In some cases, it may be necessary to consult with a specialist, such as a neurologist or neuro-ophthalmologist, to obtain a definitive diagnosis.
For individuals pursuing professional certifications, such as those offered by DRI International, it's essential to maintain your credentials through ongoing education and adherence to established standards. Unlocking your DRI digital badge and displaying your certification can enhance your online professional profile, showcasing your expertise and commitment to professional development. Maintaining your DRI International certification typically involves meeting certain requirements, such as paying an annual maintenance fee and earning continuing education activity points (CEAPs). These requirements ensure that certified professionals stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends and best practices.
In the digital age, access to information and resources is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients. Systems like MyDRSI, a comprehensive ophthalmology system, offer a structured approach to diagnosing and managing eye conditions. These systems often include standardized diagnostic protocols, personalized treatment plans, advanced technological integration, and meticulous monitoring. The affordability, quality, and unique features of such systems can make them a valuable asset in the delivery of eye care. Similarly, for individuals seeking to access institutional resources, such as ERP systems, it's important to follow the established procedures and to seek assistance if you encounter any difficulties. For example, if you have several failed attempts to log in, it's best to click on the "forgotten password" link before your account becomes disabled.
Mydriasis, while sometimes a benign finding, can also be a window into more complex underlying conditions. Whether it stems from medication side effects, recreational drug use, eye trauma, or neurological disorders, recognizing and understanding the significance of dilated pupils is vital. A prompt and thorough medical evaluation is crucial to determine the cause of mydriasis and to ensure appropriate management and treatment. By staying informed and proactive about our eye health, we can better protect our vision and overall well-being.
- Pinayflix Tv Your Ultimate Guide To Filipino Entertainment
- The Viral Buscar Kid Mom Cctv Video Whats The Buzz
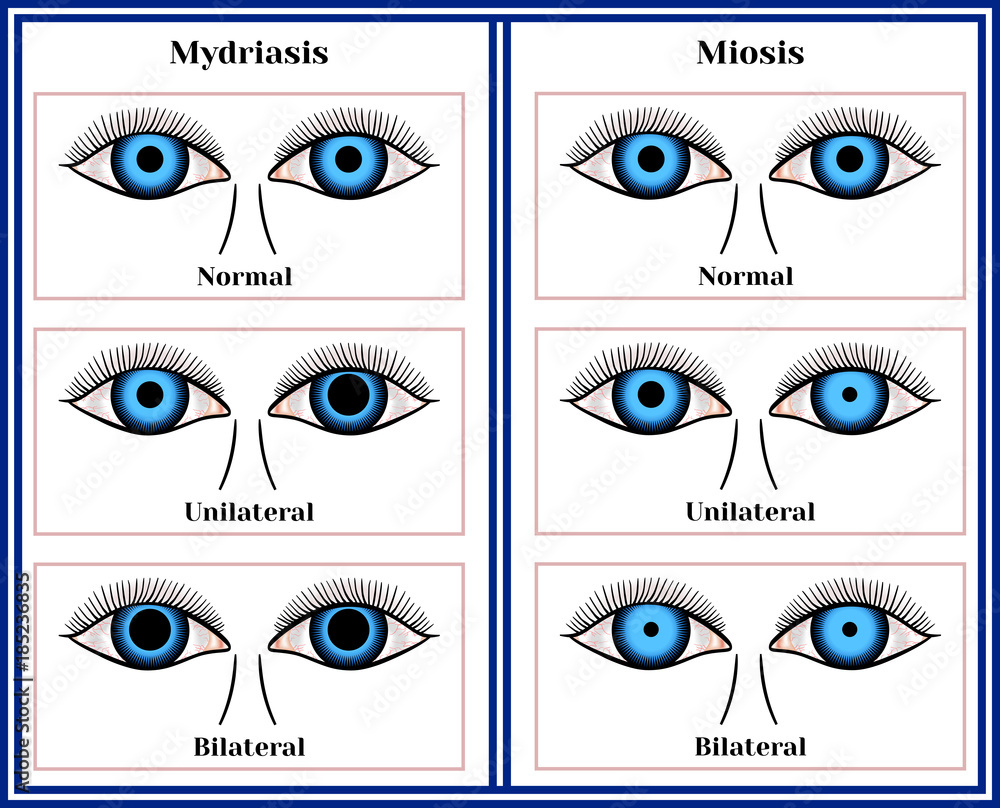
Miosis And Mydriasis
.jpg)
What Is Miosis of the Eye and How to Manage It OBN
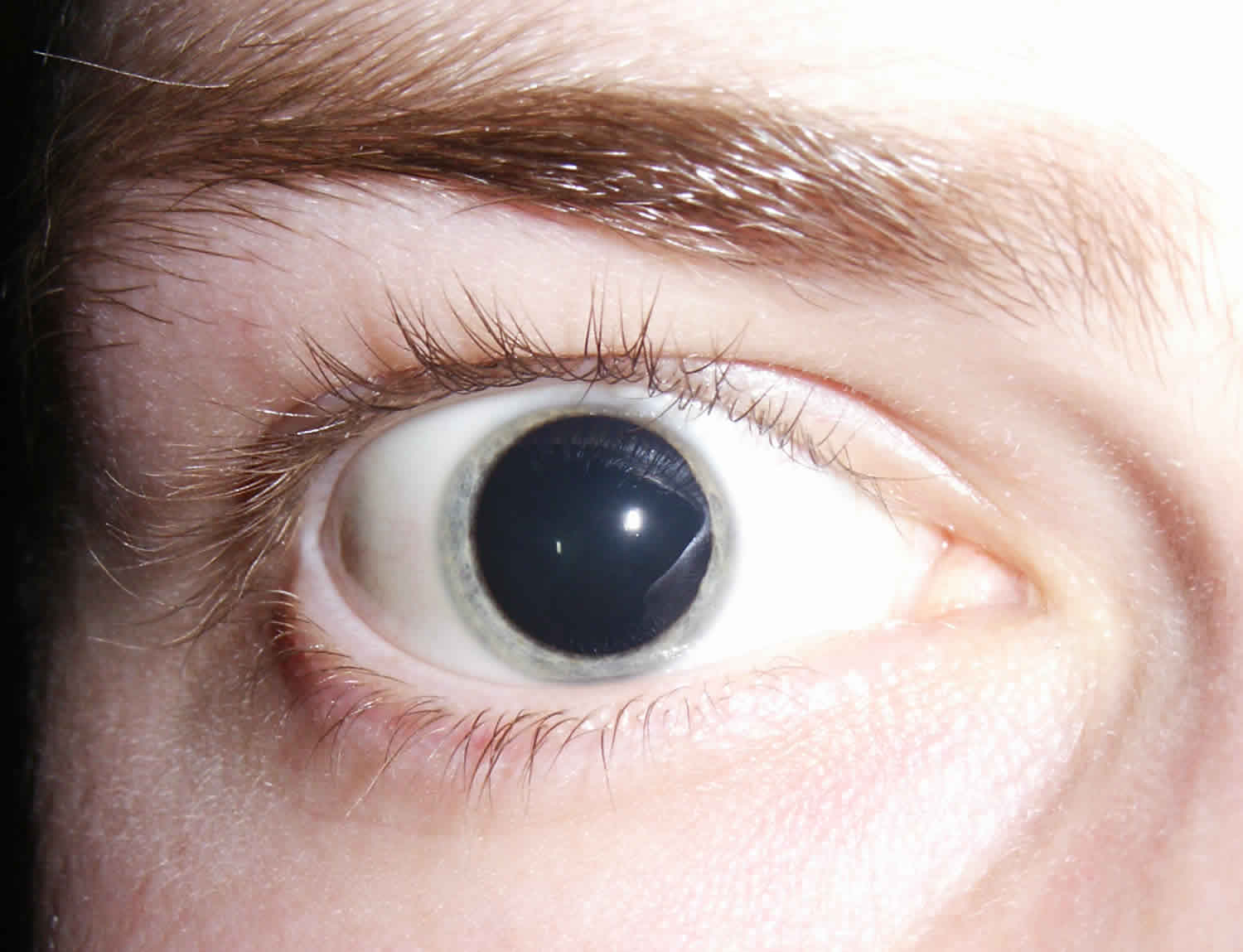
Mydriasis, mydriatic pupil causes, diagnosis & treatment